Charging Kits
These kits consist of Charge controllers, inverters and transfer switches
- Charge controllers
- Available in two types (We focus on MPPT)
- MPPT - most efficient - you can install +20% less solar panels and get the same power as PWM (essential with our fewer available daylight hours in Canada)
-
PWM - Effectively reduces your solar power output by more than 20%, so if your solar array is outputting 100W, your batteries will only see 80W (even less because panels generally can't produce what they are rated for this far North)
- Charge controllers are rated in two ways:
- The Input side (Solar Panels)
- Power in Watts
- More power = more stored energy in less time
- Voltage of the panels
- Higher voltage = more efficient and smaller (cheaper) cables
- The Output side (Battery bank)
- Battery bank voltage (12 / 24 / 48 Volt)
- Higher voltage = more efficient system and smaller (cheaper) cables
- Current to the batteries, ie 20/30/40/100 Amp
- Higher current = faster battery charging
- Inverters
- change battery voltage to house voltage (120 / 240 Volts) to run devices like laptops, TVs, coffee makers etc.
- 120 Volt inverters are more common for mobile projects
- 240 Volt inverters allow more residential style appliances to be run
- are rated in Watts or VAs (like Watts, but better at running motor loads like air conditioning, saws, etc)
- range from a few hundred watts (laptops, usb chargers) to thousands of watts (microwaves, coffee makers, heaters)
- Transfer switches
- allow backup power (from shore, generator or grid) to charge the batteries and run your devices directly
- are rated in Amps
- 30Amp would be a small trailer
- 50Amp + would be a bigger trailer
Click below to view in depth information
Our modular kits have three main parts:
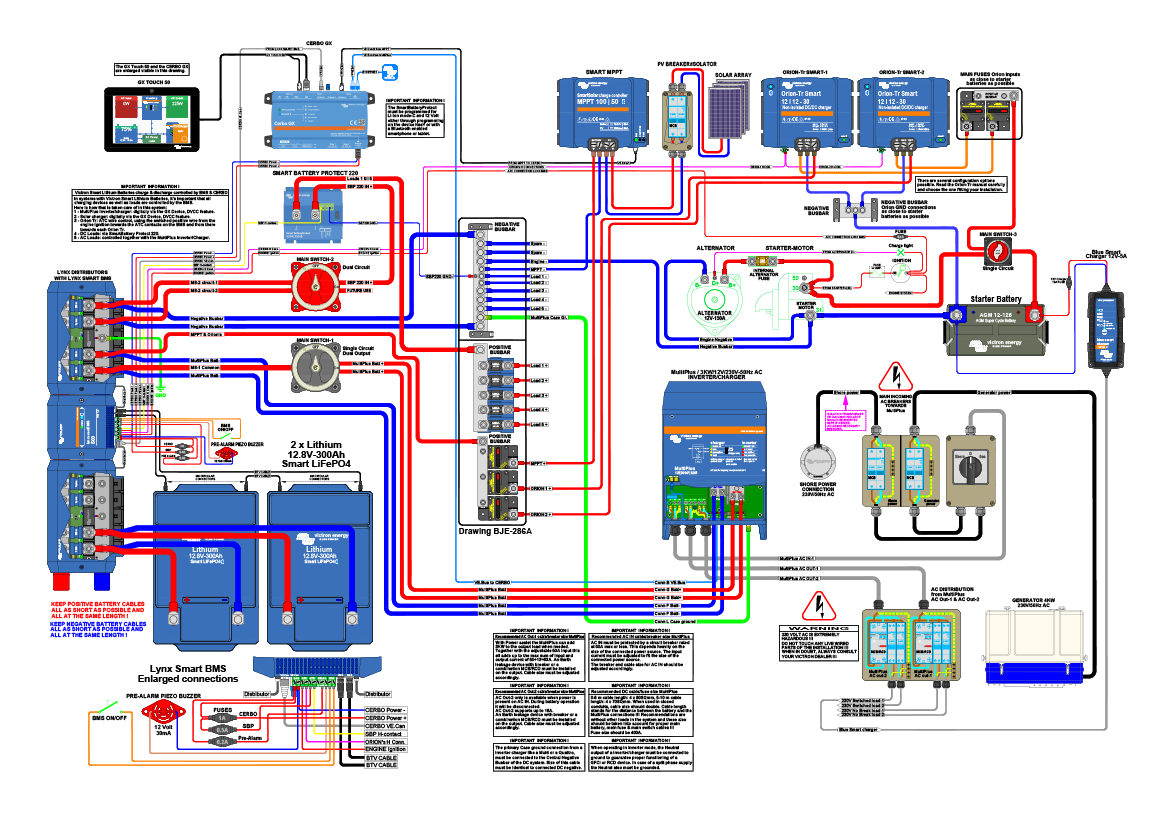
1 - Solar Panel Kits - Nature's power source
This is the exciting part of off grid living, turning nature into power you can store for later! Here are some quick pointers:
- Panels come in different types, we focus on Monocrystalline panels as they are generally just better with longer lifespans and more power production for the same Wattage which is important with the fewer hours of sun available per day in Canada. Polycrystalline can offer savings where space is not an issue.
- Ratings:
- Power (Watts): The higher the Watts the more power is produced and the bigger the panels are
- Voltage: Different voltages are available, and your panels need to match the charging / inverting system and battery bank voltages
2 - Charging / Inverting Kits - Let your solar panels charge batteries and your batteries power devices
These kits consist of Charge controllers, inverters and transfer switches
- Charge controllers
- Available in two types (We focus on MPPT)
- MPPT - most efficient - you can install +20% less solar panels and get the same power as PWM (essential with our fewer available daylight hours in Canada)
-
PWM - Effectively reduces your solar power output by more than 20%, so if your solar array is outputting 100W, your batteries will only see 80W (even less because panels generally can't produce what they are rated for this far North)
- Charge controllers are rated in two ways:
- The Input side (Solar Panels)
- Power in Watts
- More power = more stored energy in less time
- Voltage of the panels
- Higher voltage = more efficient and smaller (cheaper) cables
- The Output side (Battery bank)
- Battery bank voltage (12 / 24 / 48 Volt)
- Higher voltage = more efficient system and smaller (cheaper) cables
- Current to the batteries, ie 20/30/40/100 Amp
- Higher current = faster battery charging
- Inverters
- change battery voltage to house voltage (120 / 240 Volts) to run devices like laptops, TVs, coffee makers etc.
- 120 Volt inverters are more common for mobile projects
- 240 Volt inverters allow more residential style appliances to be run
- are rated in Watts or VAs (like Watts, but better at running motor loads like air conditioning, saws, etc)
- range from a few hundred watts (laptops, usb chargers) to thousands of watts (microwaves, coffee makers, heaters)
- Transfer switches
- allow backup power (from shore, generator or grid) to charge the batteries and run your devices directly
- are rated in Amps
- 30Amp would be a small trailer
- 50Amp + would be a bigger trailer
3 - Battery Kits - Store all that power for later
These kits are the foundation of off grid systems. Store the power you generate for wherever and whenever you are ready for it.
Batteries:
- Available in 12 / 24 / 48 Volt
- 12V is great for small systems like trailers and vans
- 24V is better when using bigger inverters to power more 120V devices, also requires smaller / less expensive cabling
- 48V is best to run residential type appliances and requires even smaller / less expensive cabling
- Rated in Amp Hours (ah) or Watt Hours (Wh)
- Watt hours are a better measurement as it tells exactly what you can run on a fully charged battery but amp hours are more common
- a 100ah Lithium LifePO4 is typically about 1200Wh usable
- a 100ah Lead Acid is typically about 600Wh usable
- Connected in two ways:
- series for more voltage (4 x 12V 100ah = 48V 100ah)
- parallel for more storage (4 x 12V 100ah = 12V 400ah)
- Lithium batteries can be heated or not heated. If they are to be exposed to outdoor temperatures they should be heated as Lithium can be used at very cold temperatures but shouldn't be charged below about 2 deg Celsius. However because they don't emit hazardous gases they can be safely stored anywhere inside an RV or cabin
This is a work in progress!
We are working to create these packages, check back soon
